What data recovery tools to buy if you want to start a data recovery business?
Free video data recovery training on how to recover lost data from different hard drives?
Where to buy head and platter replacement tools at good prices?
Data recover case studies step by step guide
I want to attend professional data recovery training courses
In NTFS file system; the files are also assigned according to clusters. A cluster must be the integral multiple of physical sector, moreover always integer powers of 2. NTFS file system does not care for about sector, nor sector size (for example not 512 bytes), but cluster size is assigned automatically according to the volume size by format program when formating.
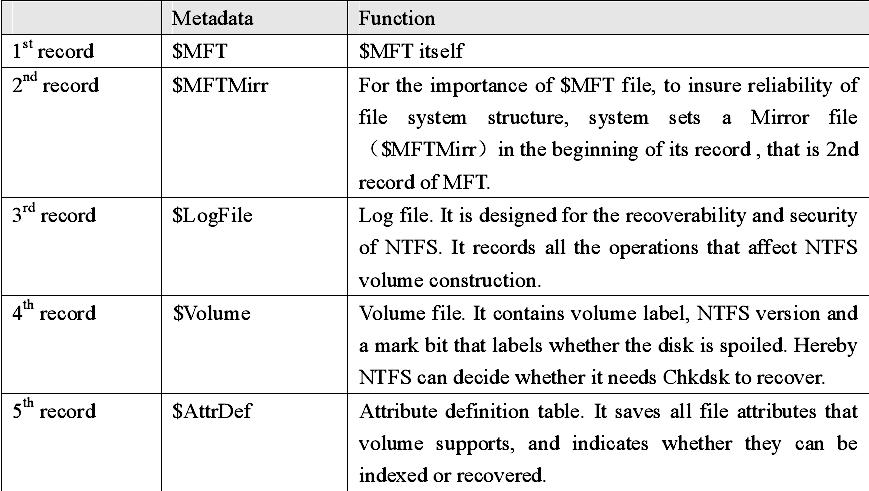
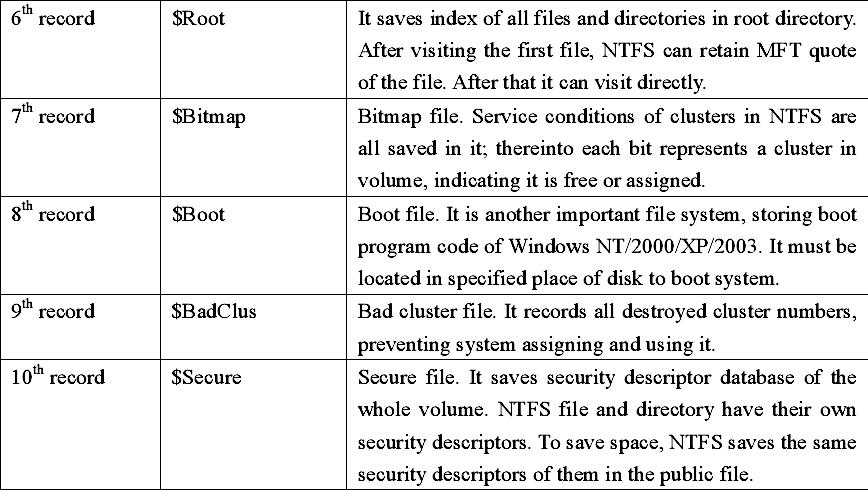
By master file table (MFT) to determine the file storage location in disk. The master file table is a corresponding database composed of series of file records—each file has a record in a volume (large files may have many corresponding records). The first file record is called basic file record with some information of other extended file records. Master file table itself also has its own file record.
Each file in NTFS volume has a unique identifier of 64 bit called file quotation number/File Reference Number. The file quotation number consists of two parts: file number and file order. The file number is 48 bit, corresponding to the position of MFT. The file order increases as repeating usage of file records, which is designed for internal consistency examination of NTFS.
NTFS locates clusters with logic cluster number (LCN) and virtual cluster number (VCN). LCN is the simple number for all clusters from beginning to end. With volume factors multiplying LCN, we can get physical byte offset in volume, thus obtaining physics disk address. VCN is the number for specified files from beginning to end, which is convenient for quoting the data of files. VCN can be mapped as LCN, but it does not request physical continuity.
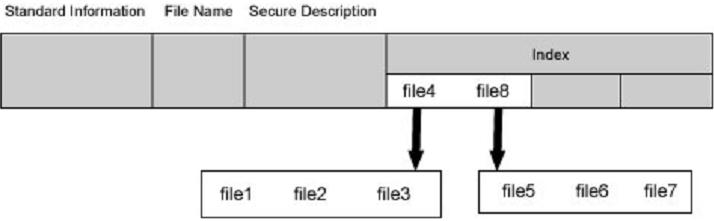
Directory of NTFS is only a simple filename and index of the file quotation number. If the directory attribute list is smaller than the length of a record, then all information of this directory are saved in the main file table records, as to that bigger than record directory, it was managed with B+ tree.
In the basic file recording of master file table, it has an indicator aiming at the index cache which is not usually used, including sub-directory and file exterior cluster, but B+ tree structure is convenient for the file and the sub-directory in large-scale table of contents.
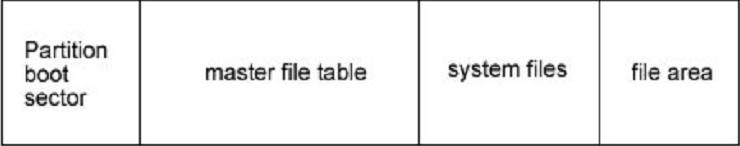
In NTFS, all data saved in the volume are contained in file, including file construction that is used to locate and obtain files, boot program and bitmap files that record volume size and service condition. This manifests the principle of NTFS: all things in disk are called files. Saving everything in files makes the file system very easy to locate and maintain data. The file fixes its storage location in disk with master file table.
The relationship of NTFS’ each region:
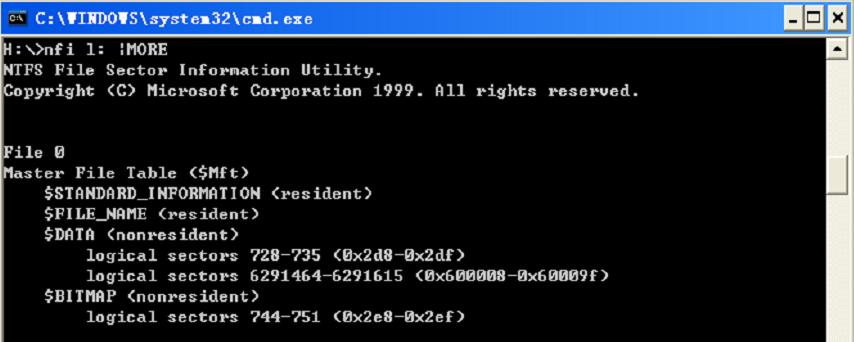
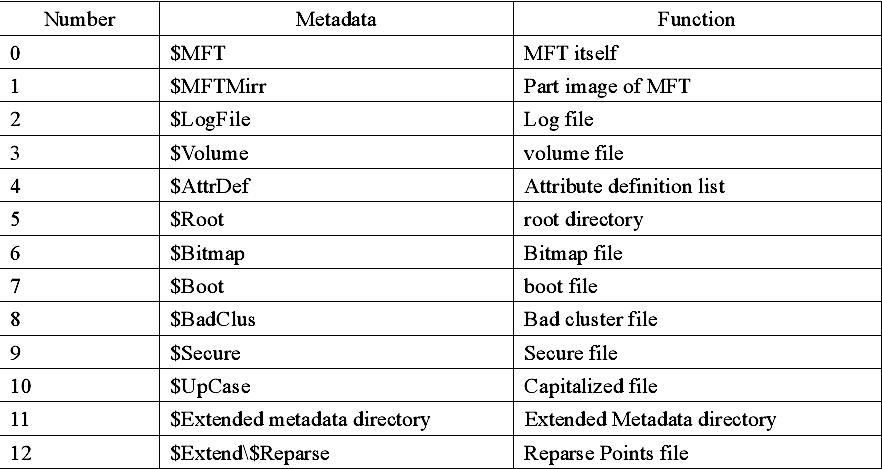
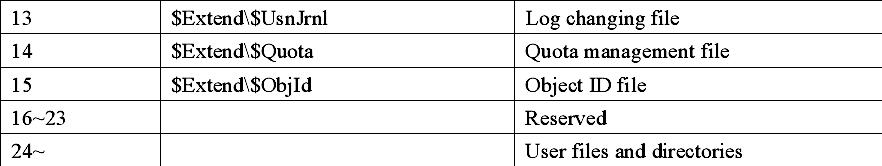
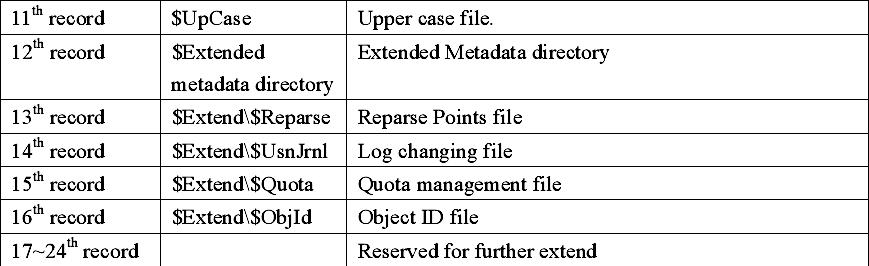
Size of file records in MFT is generally fixed. No matter the size of a cluster, the records all are 1KB, which equals to inode (i node) in Linux. File records in MFT file record array are physically continual, number from 0. Therefore NTFS can be considered as the pre-definition file system. MFT is only used by system’s organization and framework file system. This is called Metadata in NTFS. Thereinto the basic first 16 records are extremely important Metadata files used by operating system. These Metadata file names all start with “$”, the hidden files, cannot be listed in
Windows NT/2000/ XP/2003 by dir order as ordinary files. But Microsoft Corporation provides an OEM TOOL called NFI.EXE, which may demonstrates the important Metadata files of NTFS master file table. The result is as following:
Each MFT recording corresponds with different file. If a file has many attributes or be dispersed into several fragments, it is probable that it needs more file records. By now, the first record that stores its file record position is called “base file record”.
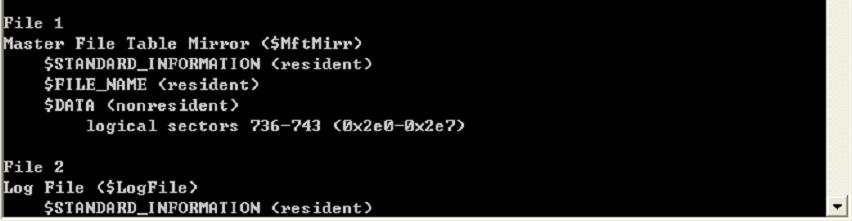
Records in $MFT
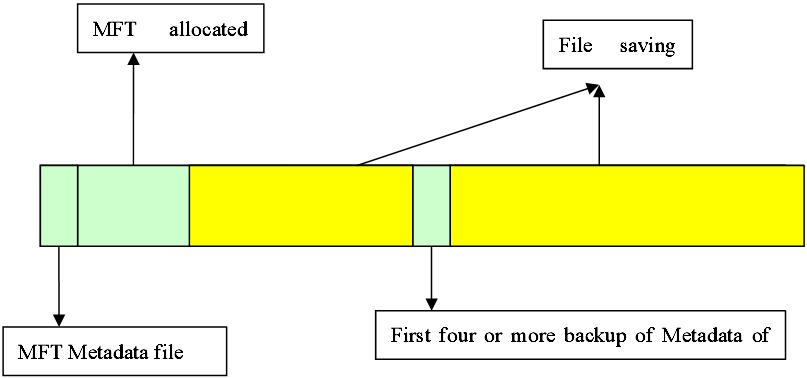
Space allocation of MFT:
NTFS volume divides disk into two major parts, in which about 12% assigned to MFT to meet unceasing growth of the file quantity. In order to maintain the continuity of Metadata in MFT, MFT enjoys the sole right to this 12% space, the rest 88% space is assigned to save files. The leavings disk space contains all physical leaving space – including that of MFT. In another word, when files use up the storage space, Windows operating system would reduce the MFT space
simply, and assign it to the file storage. When there is leavings space, it would be divided again to MFT. Although the system tries its best to maintain the dedication of MFT space, sometimes, it has to sacrifice. Sometimes although the MFT fragments are unendurable, it is unable to prevent its occurrence actually.
The process of NTFS’s visiting the volume through MFT questionnaire is as following:
First, when NTFS visits a volume, it must be “loading” this volume: NTFS will check the boot file (file defined by $Boot Metadata file), and find physical disk address of MFT.
Then, it can obtain mapping information from VCN to LCN in data attribute of file records, and save it in memory. This mapping information locates where MFT runs in disk.
The next, NTFS opens MFT records of several Metadata files, and then opens these files. If it is necessary, NTFS will start to execute file system recovery operation. After openning the leavings Metadata file in NTFS, users can visit this volume.







Comments are closed
Sorry, but you cannot leave a comment for this post.